Viewport Management
Viewport is window or texture rectangle which is destination point for rendering operations. Main window and each render target may have unlimited amount of viewports, but they almost always need at least one.
If several viewports overlap in destination texture, Viewport with higher index will take precedence.
Unless RenderPipeline clears destination region of the viewport, the initial contents are undefined.
Viewport ignores RenderPath if RenderPipeline is used.
Render Pipeline Basics
RenderPipeline is the root level scene component that manages scene rendering and keeps current rendering settings. RenderPipeline spawns one RenderPipelineView per viewport rendering this scene. RenderPipeline doesn't do any rendering logic on its own, RenderPipelineView does actual rendering.
TODO: Support of multiple RenderPipeline objects in one scene may be implemented using view masks on demand.
RenderPipeline or derived component should be present in the root node of the Scene in order to render scene. If no such component exists and legacy render is disabled, new instance of RenderPipeline component is created automatically.
Default Rendering Pipeline
Color space
Rendering in Gamma color space (i.e. without gamma correction) results in incorrect lighting and light blending. However, rendering in Gamma color space is supported on all platforms.
Rendering in Linear color space (i.e. with gamma correction) results in physically correct light blending. However, it requires hardware sRGB render target support.
Choose color space wisely: changing it results in substantial difference in resulting picture.
Gamma vs Linear color space:
Color range
Colors in Low Dynamic Range aka LDR are in range [0, 1] with fixed precision of 1/256. LDR is supported on all platforms. Also, it's easier to work with: there's no need to worry about converting final image to displayable color (no tone mapping needed).
Colors in High Dynamic Range aka HDR are in range [0, 65504] with relative precision of 1/1024. HDR enables more realistic light intensities and more correct effects like bloom or reflections.
TODO: Improve support of HDR assets.
Lighting Modes
The following aspects of lighting are always applied when geometry is rendered first time:
- Light maps;
- Light probes;
- Emission;
- Ambient lighting.
Opaque geometry lit with per-pixel lights are rendered differently for Forward and Deferred lighting.
Translucent geometry is always lit using Forward lighting.
Forward Lighting
Lighting partially is processed on CPU before rendering:
- All visible lights affecting object are sorted by importance and intensity;
- All important lights are lit per-pixel;
- Until quota of pixel lights is exceeded, automatic lights are lit per-pixel;
- Until quota of vertex lights is exceeded, remaining automatic and not important lights are lit per-vertex;
- Remaining automatic and not important lights are lit using spherical harmonics on CPU;
Geometry is first rendered with all vertex lights and all SH lights, but without any per-pixel lights (base pass). All per-pixel lights affecting geometry are rendered in each own separate pass (light passes).
Exception: at most one per-pixel directional light with positive intensity is applied in base pass as well (litbase pass).
Deferred Lighting
Geometry is rendered to geometry buffer textures just once (deferred pass). All lights are per-pixel and applied in post-processing afterwards.
Geometry buffer layout:
| Channel | Description |
|---|---|
color[0].rgba | Final color with applied ambient, emission, light maps and light probes |
color[1].rgb | Albedo color |
color[1].a | Unused |
color[2].rgb | Specular color |
color[2].a | Roughness (for PBR rendering) or specular power remapped from [0, 255] to [1, 0] (for non-PBR rendering) |
color[3].rgb | Normal in world space remapped from [-1, 1] to [0, 1] |
color[3].a | Unused |
World-space position is reconstructed from depth buffer.
Shadows
Shadows are rendering using shadow maps. Shadow maps are packed into atlases of specified size. All visible shadow maps are re-rendered on each frame from scratch (no caching).
Directional lights support up to 4 cascades (only 1 on mobile platforms).
Shadows maps may be filtered using Percentage Closer Filtering (1x1, 2x2, 3x3 or 5x5 filter kernels) or Variance Shadow Mapping.
HDR to LDR conversion
When all HDR-related effects are applied, it's necessary to convert HDR texture back to LDR.
Exposure allows to control how bright scene should be for the camera. Higher exposure – brighter picture. If auto-exposure is enabled, RenderPipeline will try to guess best exposure and smoothly adjust to it.
Tone Mapping converts HDR to LDR using some heuristic formulas. If tone mapping is disabled, HDR colors are just trimmed to [0, 1].
Gamma Correction is applied automatically in the end.
Fallback
If current platform doesn't support current settings, RenderPipeline will automatically reduce settings to closes supported configuration. It may cause visual glitches or disabled effects.
This behavior cannot be disabled. Check for minimal system requirements manually.
Properties
Common properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Space | Defines color space and color range used for color buffer. |
| > LDR Gamma | Low dynamic range, Gamma color space. |
| > LDR Linear | Low dynamic range, Linear color space. |
| > HDR Linear | High dynamic range, Linear color space. |
| Material Quality | Controls quality level used to pick technique from Material definition. |
| > Low | quality = 0 |
| > Medium | quality = 1 |
| > High | quality = 2 |
| Specular Quality | Quality of specular highlights. |
| > Disabled | No specular is calculated. Ignored in PBR shaders. |
| > Simple | Calculate specular from input data as-is. |
| > Antialiased | Apply additional heuristics to reduce specular flickering on tiny curved surfaces. |
| Reflection Quality | Quality of surface reflections. |
| > Vertex | Reflection parameters are calculated per-vertex. Resulting reflections are perfectly sharp and not affected by normal mapping effects. May be faster on mobiles. |
| > Pixel | Normal reflection with best possible quality. |
| Readable Depth | Whether the depth buffer should be readable as shader input texture. Enables advanced depth-related effects like soft particles or water depth. |
| Max Vertex Lights | Max number of per-vertex lights. Maximum is 4. |
| Max Pixel Lights | Max number of per-pixel lights. Maximum is almost unlimited. It's safe to set this number to arbitrary high number since memory is allocated on demand. |
| Ambient Mode | Ambient lighting mode used to render scene. |
| > Constant | Constant ambient is picked from Zone at camera position and applied to all visible objects. Worst quality, best performance. No per-instance overhead. |
| > Flat | Constant ambient is picked at object position. Low quality. Relatively fast. 16 bytes of per-instance overhead. |
| > Directional | Gradient ambient is picked at object position. Best quality, worst performance. 7*16 bytes of per-instance overhead. |
| Enable Instancing | Whether to enable dynamic instancing. |
| Cubemap Box Projection | Whether to use box projection for configured ReflectionProbes. |
| Depth Pre-Pass | Whether to draw objects with depth pass to depth buffer only before main scene passes. May increase performance in case of heavy pixel shaders. Depth buffer is available before scene passes. |
| Lighting Mode | Mode of used to render lit objects. |
| > Forward | Forward lighting. All materials are rendered as expected. |
| > Deferred Blinn-Phong | Deferred lighting. PBR materials may be rendered incorrectly. |
| > Deferred PBR | Deferred lighting. Non-PBR materials may be rendered incorrectly. |
| Draw Debug Geometry | Whether to draw geometry from DebugRenderer. |
Shadow properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Shadows | Whether to enable shadows. |
| PCF Kernel Size | Size of shadow smoothing filter kernel. Could be 1, 2, 3 or 5. |
| Use Variance Shadow Maps | Whether to use VSM instead of classic shadow maps. Smoother shadows, more light bleeding. |
| VSM Shadow Settings | Max variance and probability bias used by VSM. |
| VSM Multi Sample | Multi sample level used for VSM textures. |
| 16-bit Shadow Maps | Whether to use low-quality 16 bit shadow maps |
Post-processing settings
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Auto Exposure | HDR only. Whether to adjust exposure automatically. |
| Min Exposure | HDR only. Minimum possible exposure. Currently used exposure if Auto Exposure is disabled. |
| Max Exposure | HDR only. Maximum possible exposure. |
| Adapt Rate | HDR only. Rate of exposure change by Auto Exposure. |
| Bloom | Whether to enable bloom |
| Bloom Iterations | Number of blurred textures used to bloom. More iterations mean higher maximum radius of bloom effect. |
| Bloom Threshold | Minimum pixel brightness that causes bloom in post-exposure space. |
| Bloom Threshold Max | Maximum pixel brightness that contributes to bloom intensity increase. |
| Bloom Intensity | Bloom intensity multiplier. |
| Bloom Iteration Factor | Controls distribution of energy between different bloom radiuses. Higher factor means more energy for big radiuses. |
| Tone Mapping Mode | HDR only. Tone mapping used to convert HDR to LDR. |
| Post Process Antialiasing | Post-processing antialiasing algorithm used to smooth edges. |
| Post Process Grey Scale | Convert output color to shades of gray. |
Examples
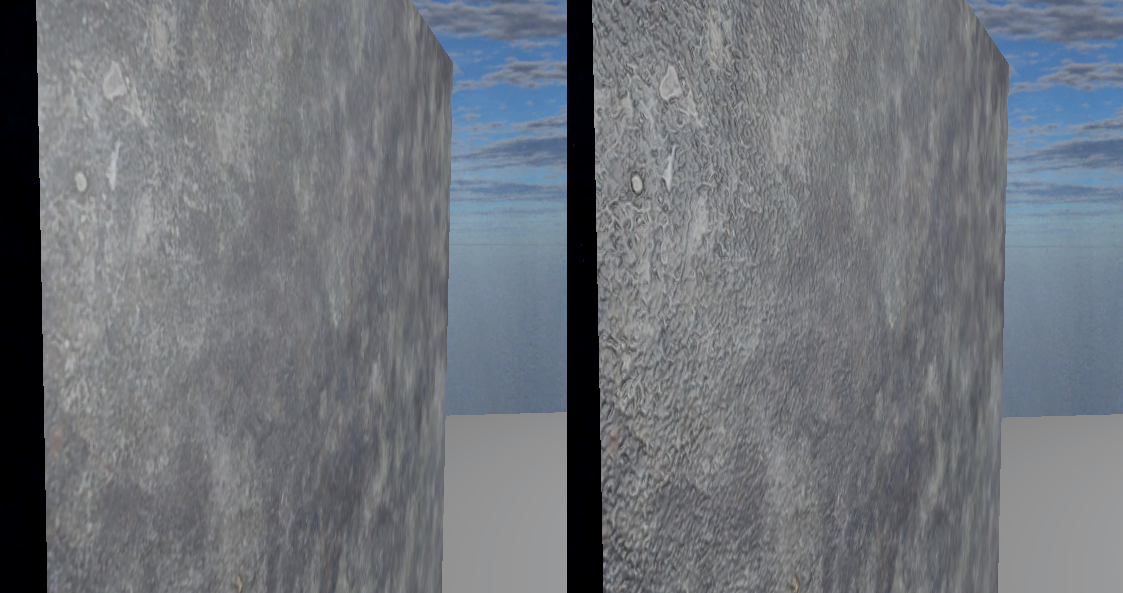
Disabled vs enabled normal mapping controlled by Material Quality:

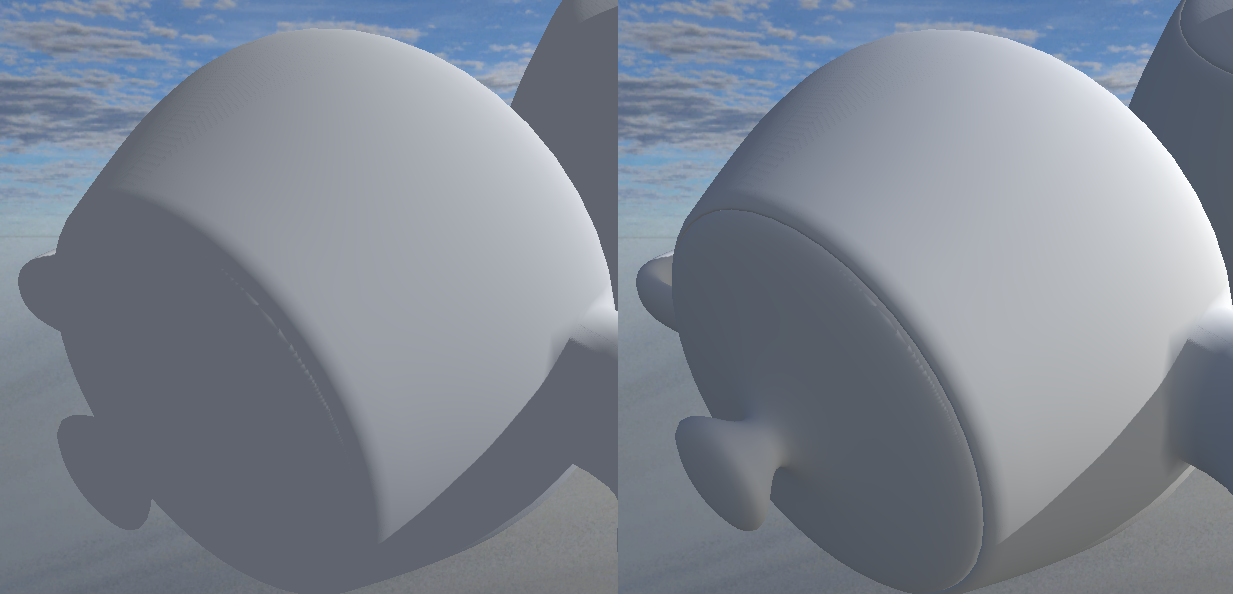
Simple vs Antialiased Specular Quality:
Vertex vs Pixel Reflection Quality:
Flat vs Directional Ambient Mode: